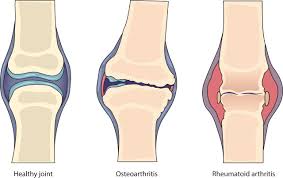
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that mainly influences the joints; rheumatoid arthritis, especially if it manifests, comes out in terms of inflammation and pain. The disease may cause damage if left unattended for a long period. Although it frequently occurs like osteoarthritis, there is a difference between the two conditions. Whereas the causative factor in the case of osteoarthritis is just a matter of wear and tear, the occurrence of RA has its basis in an immune condition where a disease follows because of attacks made by the immune system on the body tissues. RA can be very debilitating. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment are of utmost importance if its course is to be controlled.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
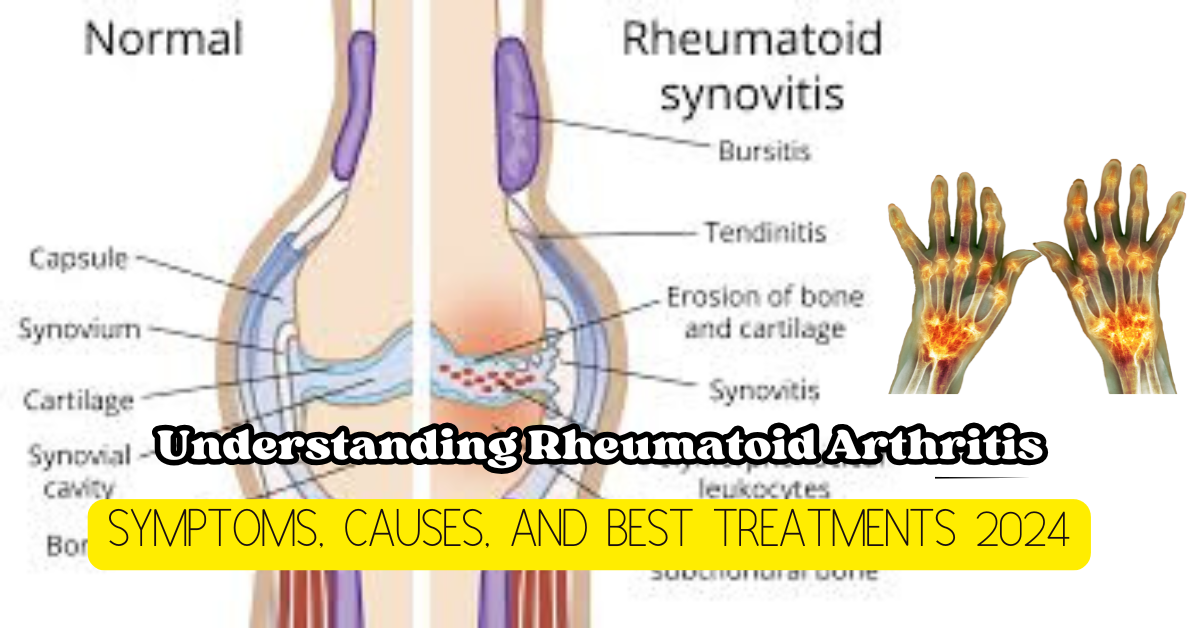
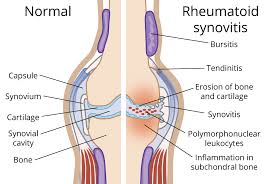
This is an autoimmune disease, meaning that immunity in the body fights infections and diseases while, in this case, mistakenly concentrating on the synovium lining of membranes of the joints and treating it as the point to be attacked. Such inflammation causes damage to cartilage and bone within the joint.
Although it occurs commonly in the hands, wrists, and knees, this disease can occur anywhere in the body, in the lungs, heart, and blood vessels. The disease progresses in deformation of the affected joints and loss of the abilities of mobilization.
Main Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA presents symptoms differently; some are far more sensitive than others. Some of the notable symptoms include;
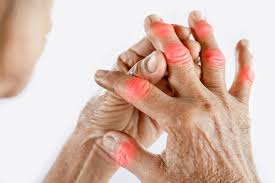
1. Arthritis with joint pain and swelling: The classic symptoms for most patients with RA comprise pain, swelling, and stiffness, and can include other joints, especially the smaller joints of the hands and feet. The pain usually is worse in the morning or after several hours of inactivity and is called morning stiffness.
2. Fatigue: Chronic fatigue is one of the usual presentations of rheumatoid arthritis. This resulted from this inflammation response, which was accompanied by pain and discomfort as the reason for draining energy.
3. Chills and Weight Loss: There may be low-grade fever and unexplained weight loss that may be associated with RA due to hyperactivity of the immune system all over the body.
4. Redness and Warmth in the Joint: The inflamed joints can become red and warm due to increased blood flow to the area of inflammation.
5. Skin Nodules: Rheumatoid nodules are firm swellings under the skin, which can form over bony prominences, such as pressure over the elbows. Nodules are a classic finding in more severe RA.
Etiology and Risk Factors
The cause of RA is unknown. However, it is assumed that several factors precipitate the disease:
1. Genetic Susceptibility
There are many susceptibility genes identified that predispose to RA. Susceptibility to infection of RA also increases among individuals with a positive family history of RA.
2. Hormonal Factors
RA has a higher incidence among females as compared to males. Such observations may indicate some hormonal predisposition since it deteriorates postpartum and improves in cases of pregnancy.
3. Environmental Factors
Some of the exposures that have been implicated as triggers include infections, smoking, and exposure to pollution in genetically predisposed individuals likely to develop the disease.
4. Age and Gender
RA can be found at any age but is more common between 40 and 60 years of age. Women are two to three times more likely to have RA than men.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosis
Early and proper diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis helps a lot in managing the disease and saving joints from getting damaged. Doctors combine different tests for diagnosing RA: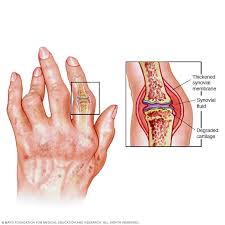
1. Physical Examination
A basic physical examination by a physician checks swelling, redness, and motion of joints. They could look for rheumatoid nodules and painful areas as well.
2. Blood Tests
Some blood tests include rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP), and high C-reactive protein (CRP). These may imply the involvement of inflammation and activity in the immune system involving RA.
3. Imaging Tests
X-rays, ultrasound, and MRI scans generally indicate the nature and grade of damage done to the joints and inflammation.
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Though RA has no cure, many treatments are aimed at minimizing the morbidity of symptoms, reducing inflammation, and preventing permanent damage inflicted on the joints. This would depend on the condition and other factors of the person involved.

1. Drugs: The use of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen lessen the pain and inflammation caused but cannot halt the progression of the disease.
- Corticosteroids: The drugs of corticosteroids, like prednisone, are used to reduce inflammation quickly. Their use is done cautiously because the conditions caused and the circumstances that go with the long-term usage of these medications are usually detestable.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): There are drugs such as methotrexate and leflunomide that modify the disease process of RA itself in its course by acting upon the basic immune response.
- Biologic Agents: Biologics are a new class of drugs that may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and halt the destruction of the joints by drugs targeting parts of the immune system. Such a drug include etanercept and infliximab.
2. Physical Therapy: The RA patients are also always advised to continue doing some form of exercise under physical therapy to prevent the building up of stiffness within the joints, develop the mobility of the joints as well and strengthen their muscles. There could be a specialist or therapist whom one could advise on what should be done to enhance the motion range and prevent stiffening of the joint.
3. Surgery: It can be combined with surgical intervention where the extreme damage of the joints calls for such interventions. Here, an individual may be subjected to the replacement of the joint, repair of the tendons, or even join in the total fusion of a joint fully and then achieve complete function free from pain.
4. Lifestyle Change: Lifestyle change accompanies the medical treatment, and it enhances overall well-being generally:
- Physically Exercise: The low-impact exercises swimming, and walking loosen the joints and keep the muscles firm.
- Healthy Diet: This diet rich in anti-inflammatory food such as fatty fish, fruits, and vegetables would help control the symptoms of RA.
- Reduction in Stress: It is believed that when people meditate or practice relaxation techniques, the condition of flare-ups of symptoms of RA is reduced.
- Prevention of Rheumatoid Arthritis flare-ups: This mostly is a periodic disease. There are periods of flare-ups and there are periods of remission. Completely preventing flare-ups is impossible, but there are means to limit flare-ups:
- Quit Smoking: This is the biggest risk factor for getting RA as well as for exacerbation of the symptoms
- Keep Healthy Weight: Obesity puts much more stress on the knees and other joints. The disease due to obesity itself tends to make worse the symptoms of RA.
- Exercise: It maintains all kinds of joint mobility through proper exercise as well as reduces the inflammation within the body due to RA.
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis
The nature of RA is usually misunderstood because it is a pretty challenging time to live with. However, the right attitude will always provide a quality of life as meaningful and rewarding. So, the patient and his or her healthcare provider would then need close cooperation to plan the course of treatment that would be tailored to specific needs, exercise regularly, and manage psychological stress. Continuous follow-up and treatment will eventually slow down the progression of disease, improve quality of life, and may even prevent complications in the long term.
I do believe that rheumatoid arthritis is life-altering. Still, with such advanced treatments and proper management, one can easily keep up an active lifestyle thus controlling the symptoms.



One thought on “Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Best Treatments 2024”